Music Macro Language
Music Macro Language or Music Markup Language is an abstract digital notation format for music. Because digital music can be made on numerous audio chips, each with unique capabilities, there is no standard format to MML. The format has always been dictated by the interpreting program and attempts to create a standard format have met with only limited success. MML can be seen in many different early computer programming languages and variations of it have been created by various game developers. Versions of it have been made for pretty much every early audio chip found in arcade games, home computers, and gaming consoles.
Specific companies like Beam Software and Color Dreams used custom forms for their Nintendo games, and even some modern day trackers use it to send audio data to the various audio chips.
Contents
Examples
Microsoft BASIC
This will play Ode to Joy on the PC Speaker.
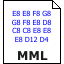
10 PLAY "O2 T120 E8 E8 F8 G8 G8 F8 E8 D8 C8 C8 E8 E8 E8 D12 D4" 20 PLAY "E8 E8 F8 C8 G8 F8 E8 D8 C8 C8 D8 E8 D8 C12 C4" 30 PLAY "D8 D8 E8 C8 D8 E12 F12 E8 C8 D8 E12 F12 E8 D8 C8 D8 P8" 40 PLAY "E8 E8 F8 G8 G8 F8 E8 D8 C8 C8 D8 E8 D8 C12 C4"
Sharp S-BASIC
This plays the Japanese song "Toryanse" on the PC Speaker in Sharp MZ-731.
10 TEMPO 4 20 A$="E5R1E3R0D3R0E3R0E1R0D1R0-G4R1" 30 B$="F3R0F1R0F1R0A3R0F1R0E1R0D1R0D1R0E5R0" 40 C$="C3R0C1R0C1R0E3R0C1R0-B1R0C1R0-B1R0-A1R0-A1-B5R0" 50 D$="E1R0E1R0E1R0E1R0E1R0E1R0D1R0E1R0E1R0E1R0D1R0-A1R0-A1R0B3R1" 60 E$="-A1R0-B1R0C1R0D1R0E1R0F1R0E1R0F3R1A3R1B1R0A1R0F3R0E3R0E1R0E4R0" 70 MUSIC A$+B$+B$ 80 MUSIC C$+C$+B$ 90 MUSIC C$+D$+E$
Tandy 1000 BASIC
This program will play the first couple bars of J.S. Bach's Fantasia and Fugue In C Minor on the Tandy 3 Voice.
10 DIM A$(3) 20 DIM B$(3) 30 DIM C$(3) 40 SOUND ON 50 PLAY "MLv15T80", "MLv14T80", "MNv15T80" 60 A$(0)="o2l6p6p6go3el12p12dl6ecl3fl12fl24edl12eagal6dl3gl12gl24fel12fco2bo3f" 70 B$(0)="o2l6p6p6p6p6p6cal12p12gl6ago3l3cl12cl24o2bal12bo3edel6o2al3o3d" 80 C$(0)="o1l1ccc" 90 A$(1)="o3l12fel3al12al24gfl12edegl6bl12agl6fl2o4c" 100 B$(1)="o3l12dl6co2l12bo3cdo2l3bl6bo3l12dcl3cl12cdefge" 110 C$(1)="o1l1cc" 120 A$(2)="o4l6cl12p12co3bo4co3l6bl12o4co3bagfl3gl6fp6e" 130 B$(2)="o3l12fcl3fl12fl24edl3el12el24dcbcbcl6dl12dl24cbl6cl12db" 140 C$(2)="o1l1cl2cl3cl6o2c" 150 FOR N = 0 TO 2 160 PLAY A$(N), B$(N), C$(N) 170 NEXT 180 END
NES
Here is an example of a song written for the NES.
#TITLE Song Title
#COMPOSER Composer
#PROGRAMER Copyright
@v0 = { 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 }
@v1 = { 15 15 14 14 13 13 12 12 11 11 10 10 9 9 8 8 7 7 6 6 }
@v2 = { 15 12 10 8 6 3 2 1 0 }
@v3 = { 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 }
@DPCM0 = { "samples\kick.dmc",15 }
@DPCM2 = { "samples\snare.dmc",15 }
ABCDE t150
A l8 o4 @01 @v0
A [c d e f @v1 g4 @v0 a16 b16 >c c d e f @v1 g4 @v0 a16 b16 >c<<]2
C l4 o3 q6
C [c e g8 g8 a16 b16 >c8 c e g8 g8 a16 b16 >c8<<]4
D o0
D [@v2 b @v3 e @v2 b @v3 e @v2 b @v3 e @v2 b @v3 e8 @v2 b8]4
Music-V Language
Music-V is a special type of MML used on Atari audio chips. It is similar to that of composing on a staff. You write the note, the octave, and the length. For example, C3Q (Note: C, Octave 3, Quarter Note).
Hexadecimal
Many custom MMLs would have users writing their music into long strings of hexadecimal numbers which the audio driver would convert into musical notes and effects. Each driver had a particular format that the numbers were expected to be in.
Players
Since this isn't a specific format, there are no specific players.
Games
Links
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Music_Macro_Language - Wikipedia.